Lens ring joint flanges are specialized components designed for extreme service. They create a superior seal in high-pressure and high-temperature piping systems, such as those in oil and gas, petrochemical, and offshore industries.
This guide explains their key specifications, how they work, and how they differ from other flange types.
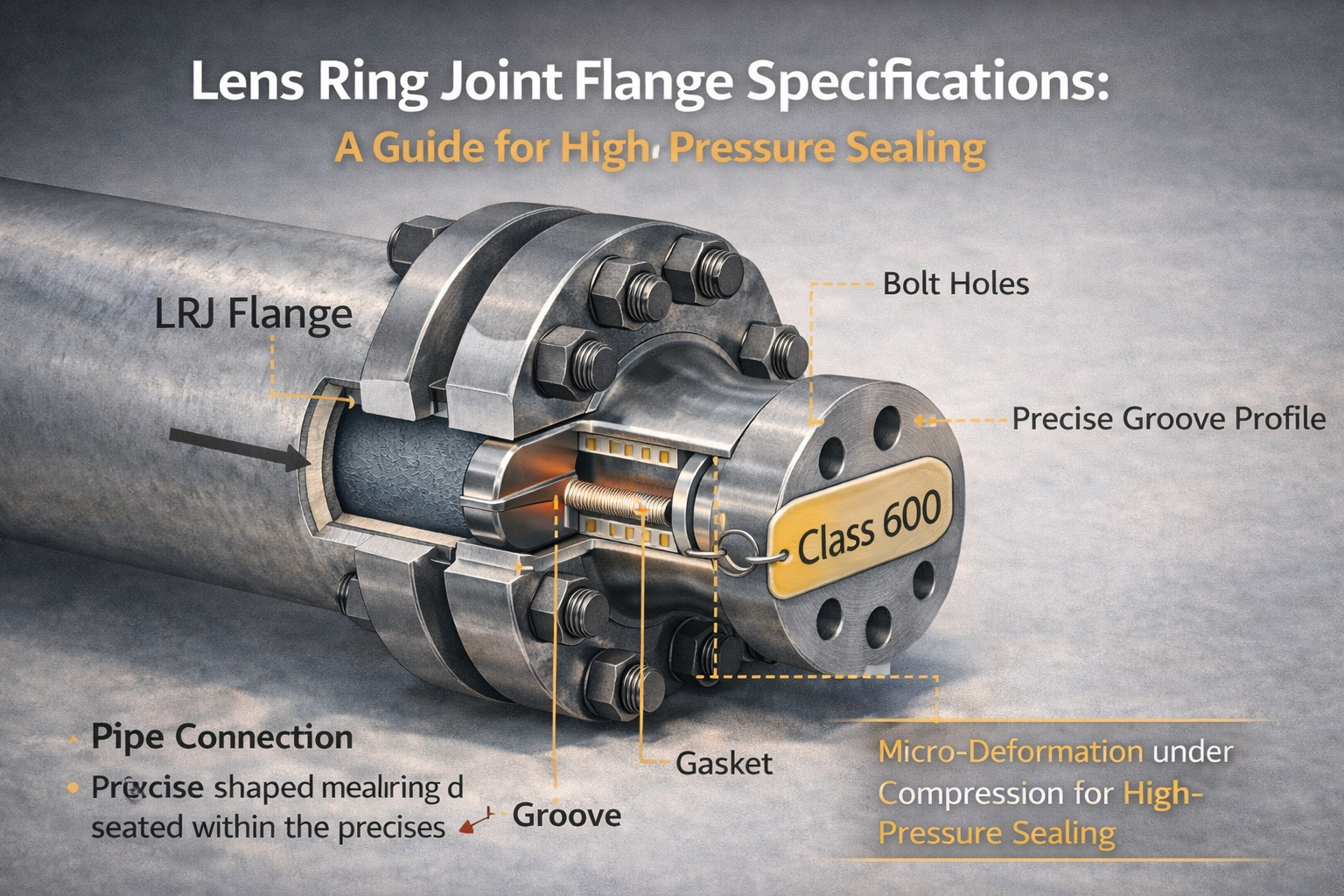
How a Lens Ring Joint Flange Works
A lens ring joint system uses a unique design. Unlike a standard raised face flange, the flange sealing face is machined at a 20° angle toward the center. A matching metal lens ring gasket, which has a spherical surface, sits between these angled faces.
When the bolts are tightened, the lens ring deforms to create a tight, line-contact seal. Higher internal pressure forces the angled faces together, which increases the contact area and improves the seal further.
Key Specifications and Standards
Lens ring joint flanges and gaskets are governed by precise international standards that define their dimensions, materials, and performance.
Primary Governing Standards:
- ASME B16.5: The main American standard for pipe flanges, which includes requirements for ring-type joint facings.
- DIN 2696: A common German standard specifically for lens ring joints, often referenced alongside ASME for these components.
- ASME B16.20: This standard covers the specifications for the metal ring gaskets used in these joints.
Critical Dimension Tables:
The precise machining of the flange groove and matching gasket is critical. Dimensions are defined by a Groove Number (e.g., R23, R37), which correlates to the Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) and pressure class. Key dimensions include the Pitch Diameter (P), Groove Depth (E), Groove Width (F), and the Radius at the bottom of the groove (R).
Sample ASME B16.5 RTJ Groove Dimensions (Class 150 & 300)
| NPS | Class | Groove No. | Pitch Diameter (P) mm/in | Depth (E) mm/in | Width (F) mm/in | Radius (R) mm/in |
| 2 | 150 | R22 | 82.55 / 3.25 | 6.35 / 0.25 | 8.74 / 0.344 | 0.8 / 0.031 |
| 2 | 300 | R23 | 82.55 / 3.25 | 7.92 / 0.312 | 11.91 / 0.469 | 0.8 / 0.031 |
| 4 | 300/400/600 | R37 | 149.23 / 5.875 | 7.92 / 0.312 | 11.91 / 0.469 | 0.8 / 0.031 |
Materials and Pressure Ratings:
Flanges are commonly made from forged materials like ASTM A105 (carbon steel) or ASTM A182 (stainless steel, alloy). Lens ring gaskets are made from a softer metal than the flange, such as soft iron or SS316, to ensure proper deformation.
Pressure ratings follow the standard class system (150, 300, 600, up to 2500). It is crucial to remember that the maximum allowable working pressure depends on both the pressure class and the material’s temperature rating.
Lens Ring vs. Standard RTJ: A Comparison
While both are for high-pressure service, the lens ring design offers specific advantages and differences.
Lens Ring Joint vs. Standard Ring-Type Joint (RTJ)*
| Feature | Lens Ring Joint Flange | Standard RTJ Flange (Oval/Octagonal) |
| Sealing Face | 20° angled face. | Flat, machined groove with parallel sides. |
| Gasket Cross-Section | Spherical (“lens” shape). | Oval or octagonal ring. |
| Contact & Sealing | Initial line contact that expands under pressure. | Broad contact area from the start as the gasket deforms into the groove. |
| Key Advantage | Requires lower bolt load to achieve a seal; gasket can sometimes be reused. | Extremely robust, considered the most efficient seal for severe cyclic service. |
| Typical Use | High-pressure valves, vessel connections, critical instrument lines. | Wellheads, Christmas trees, and main process lines in refineries. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the main advantages of using a lens ring joint?
A: The main advantages are reliable performance under very high pressure and temperature, and the ability to achieve a tight seal with a relatively lower bolt load compared to other flange types.
Q: What are the disadvantages or challenges?
A: The system is expensive due to precise machining requirements. Disassembly can be difficult as flanges must be forced apart to unseat the gasket, requiring physical space. It is not typically used for very large pipe diameters.
Q: Can I use a standard oval RTJ gasket in a lens ring joint flange?
A: No. The flange face angles and gasket shapes are completely different and are not interchangeable. Using the wrong gasket will result in a failed seal.
Q: How do I specify or order a lens ring joint flange?
A: You must provide the complete specification: Nominal Pipe Size (NPS), Pressure Class (e.g., 600#), Flange Type (e.g., Weld Neck), Material (e.g., A105), and the relevant Groove Number. For gaskets, the material and specific dimensional drawing are required.
Q: What maintenance should be considered?
A: During reassembly, always use a new gasket or one certified for reuse. Inspect the machined groove faces for scratches or corrosion, as surface finish is critical for sealing. Follow controlled bolt-tightening procedures.
Conclusion
Lens ring joint flanges provide a critical, high-integrity sealing solution for the most demanding industrial applications. Their specialized design, governed by strict standards like ASME B16.5 and DIN 2696, ensures safety and reliability under extreme pressure and temperature. Success depends on precise specification, correct material pairing, and proper installation.
Need precision-manufactured lens ring joint flanges or components for your critical service application? Our expertise covers the exacting specifications required for these high-performance systems. Submit your project requirements for a quote or technical discussion: http://texasflange.com/lp12/